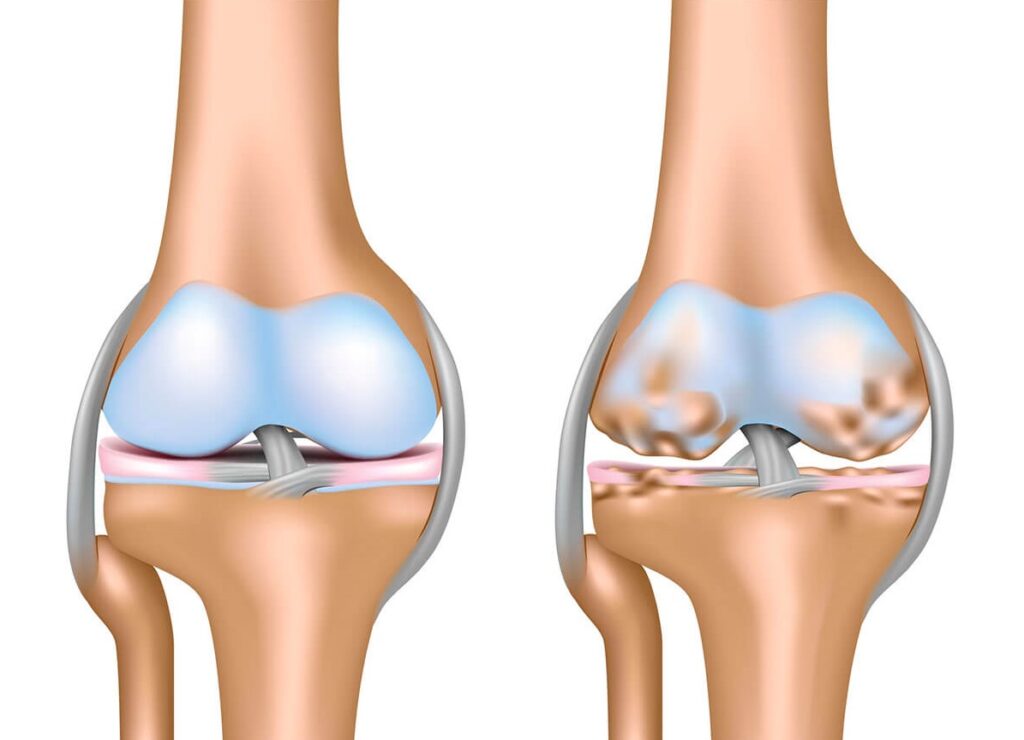
What is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, a condition that causes the breakdown of cartilage in the joints. Cartilage acts as a cushion, allowing smooth movement of the joints. When it deteriorates, bones can rub together, leading to pain, swelling, stiffness, and loss of movement. OA commonly affects the knees, hips, hands, and spine.
Who is Affected?
Osteoarthritis typically affects older adults, but it can also develop in younger individuals due to injury, overuse of joints, or genetic factors. The risk increases with age, and women are more likely than men to develop OA, particularly after menopause.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis:
The symptoms of osteoarthritis can vary from person to person but often include:
• Joint pain: Pain is usually worse after activity or at the end of the day.
• Stiffness: Especially after periods of rest or in the morning.
• Swelling: In the affected joints due to the inflammation.
• Decreased range of motion: Difficulty moving the joint as freely as before.
• Crepitus: A grating or crackling sound when the joint moves.
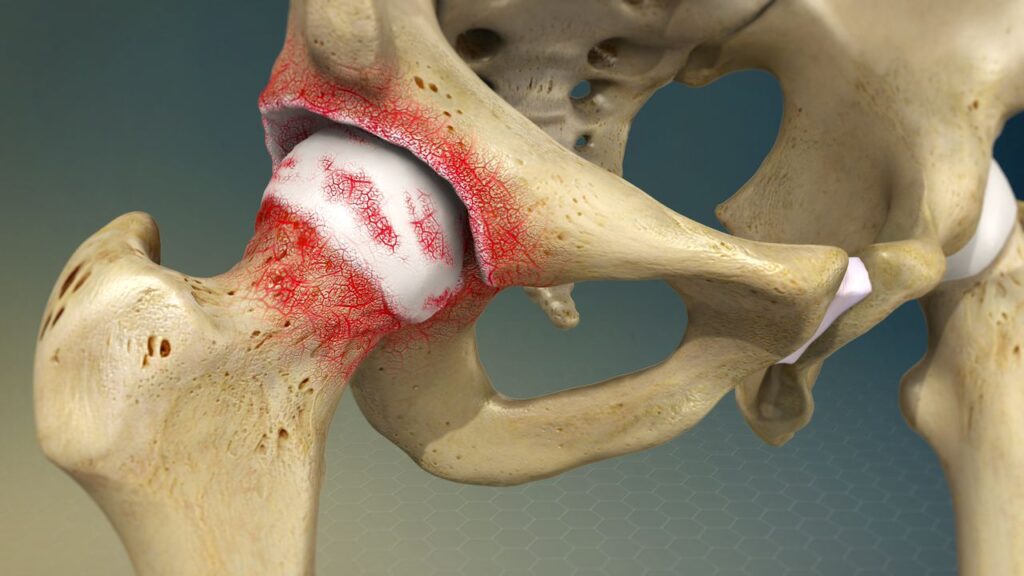
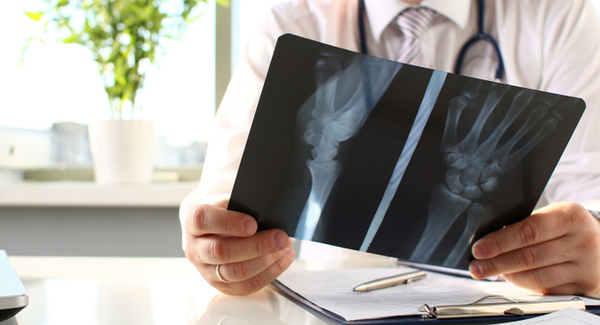
Tests for Osteoarthritis:
Diagnosing osteoarthritis typically involves a combination of a physical examination and imaging tests:
X-rays: To assess joint space narrowing, bone spurs, and other signs of joint damage.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Used to get detailed images of the cartilage, bones, and soft tissues in the joint.
Joint fluid analysis: To rule out other types of arthritis, such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis.
How is Osteoarthritis Treated and Managed?
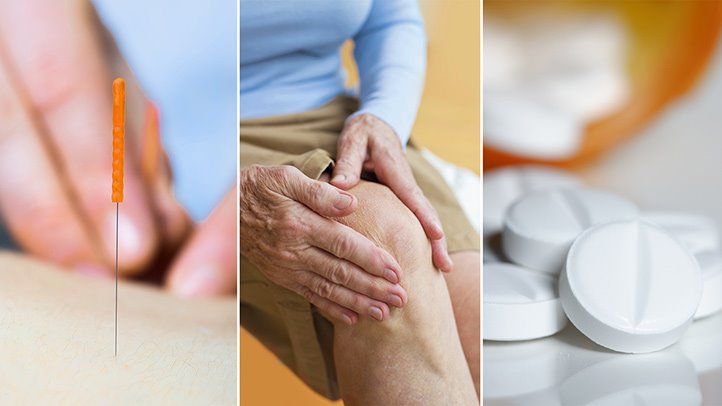

Treatment Options:
The primary goals in osteoarthritis treatment are to reduce pain, improve joint function, and slow the progression of the disease. Treatment options include:
1) Medications:
• Pain relievers: Over-the-counter options like acetaminophen or NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen) can help manage pain and inflammation.
• Topical treatments: Creams and ointments that can be applied directly to the affected joints for pain relief.
• Corticosteroid injections: To reduce inflammation in the joint and provide temporary pain relief.
• Hyaluronic acid injections: To lubricate the joint and improve mobility.
2) Physical Therapy:
Exercises to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected joints. A physical therapist can recommend joint protection techniques and strategies to improve mobility.
3) Assistive Devices:
Braces, splints, or orthotic insoles may be recommended to help support joints and alleviate stress on the affected areas.
4) Surgery:
In severe cases, surgical options may be considered, including:
• Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure to remove damaged tissue or realign the joint.
• Joint replacement surgery: Particularly for hip, knee, or shoulder joints, replacing the damaged joint with an artificial one.
Self-Help Measures:
Managing systemic sclerosis often requires lifestyle changes and self-care:
• Eat smaller meals: Six small meals a day can prevent excessive pressure on the stomach, reducing symptoms like heartburn.
• Eat slowly and chew thoroughly: Helps to manage difficulty swallowing.
• Drink plenty of water: Stay hydrated to help with digestion.
• Avoid large meals at night: Eating smaller meals earlier in the day can help prevent reflux symptoms.
• Elevate the head of the bed: This can help prevent acid reflux during sleep.
• Keep warm: Use mittens, sweaters, and other warm clothing to manage sensitivity to cold.
• Regular exercise: Helps prevent joint contractures and maintain mobility.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for systemic sclerosis focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications:
• Pain management: Painkillers and NSAIDs can help alleviate joint and skin discomfort.
• Stomach protection: Medications for acid reflux and digestive problems.
• Skin care: Moisturizing agents and topical treatments for skin thickening.
• Steroids: Used to reduce inflammation in some cases.
• Immunosuppressive agents: To control the overactive immune response.
• Blood pressure and cholesterol-lowering medications: If needed, to manage cardiovascular risk factors.
